Are you teaching MS-ES1-1: the Earth-Sun-Moon relationship, including lunar phases and tides? We have some fun activities for doing this while incorporating creative ways to highlight Earth Day in the classroom.

Understanding the Earth-Sun-Moon system is fundamental in middle school science education, but by expanding to include lunar phases and tides, we can enhance relevance and engagement. To seamlessly integrate these topics into your curriculum, we’ve compiled practical strategies and engaging activities, from hands-on model building to interactive simulations.
Additionally, we’ll explore ways to connect these lessons to Earth Day celebrations, emphasizing environmental stewardship and promoting a deeper appreciation for our planet. Let’s get started.
Part 1. Teaching the Earth-Moon-Sun Relationship for MS-ES1-1

Introducing the Earth-Sun-Moon relationship lays the groundwork for understanding fundamental celestial interactions. To make this abstract concept more tangible, you can employ various hands-on activities that cater to diverse learning styles.
One effective approach to teaching MS-ES1-1is model building, where students create scale models of the Earth, Moon, and Sun and then manipulate their positions to understand phenomena like lunar phases and eclipses.
For instance, in the “Lunar Lollipops: Reproducing the Moon Phases” activity by Teach Engineering, students work in pairs to explore the relative positions of the Earth, Sun, and Moon that result in different lunar phases. Using Styrofoam balls attached to pencils as makeshift “lollipops” to represent the Moon, students manipulate the position of the Moon around themselves while a hanging lightbulb serves as the Sun.
By rotating the “Moon” and observing its appearance from different angles, students discover the various phases and record their findings on a worksheet. This hands-on exercise allows students to visually grasp the relationship between the positions of celestial bodies and the resulting lunar phases, reinforcing concepts of Earth-Sun-Moon interactions.
Interactive simulations are another engaging tool to illustrate celestial interactions. You can utilize digital simulations or create interactive activities using simple materials. For example, students could act out the orbits of the Earth, Moon, and Sun in the classroom, with each student representing one of the celestial bodies.
By physically moving around the classroom and interacting with their peers, students can gain a deeper understanding of concepts such as rotation, revolution, and the changing positions of celestial bodies relative to each other.
Furthermore, incorporating multimedia resources such as videos, animations, and virtual reality experiences can enhance students’ comprehension of the Earth-Sun-Moon relationship. You can curate or create multimedia presentations that visually depict concepts like the tilt of the Earth’s axis, the phases of the Moon, and the occurrence of solar and lunar eclipses.
These multimedia resources complement hands-on activities by appealing to visual and auditory learners and provide additional context for understanding celestial phenomena.
By integrating various hands-on activities, interactive simulations, and multimedia resources, we can effectively teach the Earth-Sun-Moon relationship.
Part 2. Lunar Phases with Moon Phase Oreo Activity for MS-ES1-1

The “Moon phase Oreo cookie” activity is a delectable journey into the world of lunar phases, perfect for engaging middle school students in science class. With a step-by-step guide, you can effortlessly lead students through crafting edible models of the lunar cycle using Oreo cookies.
This hands-on approach to teaching MS-ES1-1 transforms abstract concepts into tasty treats by allowing students to physically manipulate the cookies to represent the different phases of the Moon.
As students assemble their Oreo models, they gain a deeper understanding of lunar phases and develop important skills such as observation, critical thinking, and collaboration. Encouraging discussion and exploration during the activity can promote active engagement and reinforce key concepts.
Plus, the allure of working with cookies adds an element of excitement to the learning experience, ensuring that students remain enthusiastic and eager to participate.
Moreover, the visual and tactile nature of the “Moon phase Oreo cookie” activity enhances comprehension and retention of the material. As students observe the changing appearance of their Oreo models throughout the lunar cycle, they internalize the relationship between the positions of the Earth, Moon, and Sun.
Part 3: Moon-Phase-Induced Tides Activity for MS-ES1-1

Engaging middle school students in activities demonstrating how lunar phases influence tides is crucial for deepening their understanding of this intricate phenomenon. One exemplary MS-ES1-1 activity is the Tide-O-Matic, offered by the Exploratorium. The Tide-O-Matic activity involves building a simple model to investigate the influence of the sun and moon on Earth’s tides.
This model consists of paper templates representing the Earth, sun, and moon, which are assembled and manipulated to simulate the gravitational forces responsible for tidal patterns.
In the first part of the Tide-O-Matic activity, participants explore solar tides by rotating the Earth around the sun and observing tidal bulges. By manipulating the model, students can visually grasp how the sun’s gravitational force creates tidal patterns on Earth’s oceans.
The moon is introduced in the second part of the activity, and the alignment of solar and lunar tides during different moon phases is examined. Students can observe how the gravitational forces from both the sun and the moon interact to create variations in tidal patterns throughout the lunar cycle. This hands-on exploration helps students understand the relationship between lunar phases and tidal behavior.
Through the Tide-O-Matic activity, students gain insights into how gravitational forces from the sun and moon create two high tides and two low tides each day, with variations influenced by the positions of celestial bodies.
Additionally, the activity provides a simplified model for understanding the equilibrium theory of tides, highlighting the complexities of real-world tidal phenomena. By engaging in this interactive learning experience, students develop a deeper appreciation for the interconnectedness of celestial bodies and Earth’s dynamic systems.
Part 4: Predicting Tides with Earth's Position and Lunar Phases for MS-ES1-1
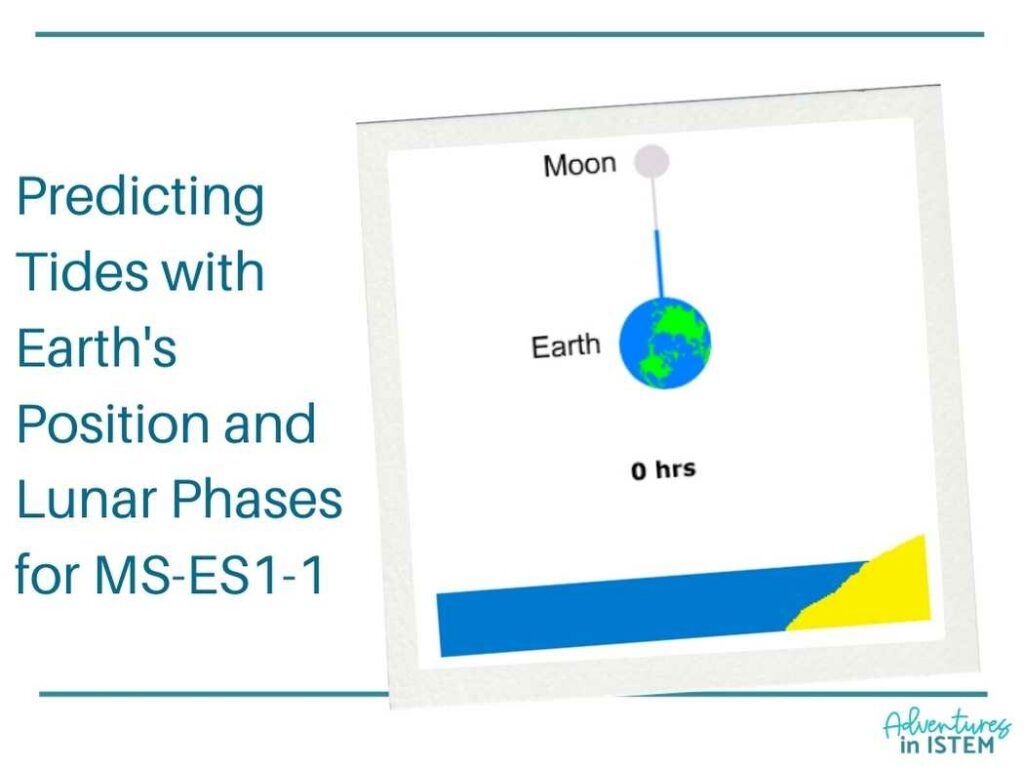
It’s important to explain how Earth’s position relative to the Sun, combined with lunar phases, affects tidal patterns. To make this concept accessible, you can utilize straightforward methods that engage students and foster comprehension.
One effective approach is to teach students how to predict high and low tides using interactive demonstrations and real-world examples.
First, in the “Predicting the Tides” activity from Ocean Explorer NOAA, participants learn how to forecast tidal patterns, which is crucial for various coastal activities. They explore how the positions of the sun, moon, and Earth affect tides.
Participants observe the timing and heights of tides, noting differences between spring tides (when the sun and moon are aligned) and neap tides (when they’re at right angles). They also see how the moon and Earth’s orbits influence tide heights over time.
The activity ends with a hands-on scenario where participants act as ship captains, navigating under a bridge based on tidal predictions. Students gain practical knowledge about tidal behavior and its real-world significance through this activity.
Next, you can guide students through practical exercises to predict high and low tides. For example, we can utilize tide charts or online resources that provide real-time tidal data for specific locations.
By analyzing these resources, students can identify patterns and correlations between lunar phases, Earth’s position relative to the Sun, and tidal patterns. Encourage students to make predictions based on their observations and compare them with actual tidal data, fostering critical thinking and data analysis skills.
Here are a few websites that provide real-time tidal data:
* National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) Tides & Currents: NOAA delivers a comprehensive online database of tidal predictions and observations for locations across the United States. Users can search for tidal data by location, date, and tide station.
* Tide Charts: Tide Charts is a website that offers real-time tidal predictions and observations for various coastal locations worldwide. Users can search for tidal data by location and view tide charts for specific dates.
By providing clear explanations, real-world examples, and hands-on learning opportunities, we can enhance students’ understanding of how Earth’s position relative to the Sun, combined with lunar phases, affects tidal patterns.
Part 5: Earth Day: Tides and Animal Reproduction

Connecting the importance of tides to Earth Day celebrations presents a meaningful opportunity to highlight the significance of environmental stewardship. One effective approach is to engage students in activities that explore how tides impact animal reproduction and ecosystems.
To begin, you can guide students in exploring specific examples of how tides influence animal reproduction. For instance, students could research and present case studies on species such as horseshoe crabs, whose reproductive cycles are closely tied to tidal patterns.
By studying these examples, students can gain insight into the importance of tides for maintaining healthy populations of marine organisms.
Next, you can facilitate discussions on the broader ecological implications of tides. Students can examine how tidal cycles impact nutrient cycling, sediment transport, and coastal erosion, all of which play crucial roles in shaping coastal ecosystems.
Through these discussions, students can better understand the interconnectedness of Earth’s systems and the vital role that tides play in maintaining ecological balance.
Finally, you can encourage students to brainstorm ways to contribute to environmental stewardship in their communities. Students could create action plans to reduce plastic pollution, conserve water resources, or participate in beach clean-up efforts.
By empowering students to take action, educators can instill a sense of responsibility for protecting Earth’s natural resources and fostering a sustainable future.
Connecting the importance of tides to Earth Day celebrations and engaging students in activities exploring the ecological significance of tidal patterns can inspire a deeper appreciation for the planet and the importance of environmental conservation.
Through hands-on learning experiences and meaningful discussions, students can develop the knowledge, skills, and motivation to become Earth stewards and advocate for positive change in their communities.
The journey through teaching the Earth-Sun-Moon relationship, lunar phases, tides, and Earth Day activities offers countless opportunities for engaging middle school students in science education.
We can deepen students’ understanding of these intricate concepts by employing hands-on activities, interactive simulations, and real-world examples while fostering curiosity and environmental stewardship.
From creating edible models of lunar phases with Oreo cookies to exploring tidal patterns through interactive simulations, exploring celestial phenomena and Earth’s dynamic systems is enlightening and enriching.
As we strive to instill a sense of responsibility for protecting our planet, let us continue to empower students to become advocates for positive change and stewards of Earth’s natural wonders.
Together, we can nurture a generation of scientists and environmentalists passionate about understanding the universe and preserving its beauty for generations.
Other blog posts you might like: